2. DAO 支持
预计阅读时间: 7 分钟The Data Access Object (DAO) support in Spring is aimed at making it easy to work with data access technologies (such as
JDBC, Hibernate, or JPA) in a consistent way.
Spring 中的数据访问对象(DAO)支持旨在以一致的方式轻松地与数据访问技术(如 JDBC、Hibernate 或 JPA)协同工作。
This lets you switch between the aforementioned persistence technologies fairly easily, and it also lets you code
without worrying about catching exceptions that are specific to each technology.
这使您能够轻松地在上述持久化技术之间切换,并且它还允许您编码时无需担心捕获到特定于每种技术的异常。
(#dao-exceptions)2.1. Consistent Exception Hierarchy
2.1. 一致的异常层次结构
Spring provides a convenient translation from technology-specific exceptions, such as SQLException to its own
exception class hierarchy, which has DataAccessException as the root exception. These exceptions wrap the original
exception so that there is never any risk that you might lose any information about what might have gone wrong.
Spring 将特定技术的异常,如 SQLException ,方便地转换为它自己的异常类层次结构,其中 DataAccessException
作为根异常。这些异常封装了原始异常,以确保永远不会丢失任何关于可能发生错误的信息。
In addition to JDBC exceptions, Spring can also wrap JPA- and Hibernate-specific exceptions, converting them to a set of
focused runtime exceptions.
除了 JDBC 异常之外,Spring 还可以包装 JPA 和 Hibernate 特定的异常,将它们转换为一系列专注的运行时异常。
This lets you handle most non-recoverable persistence exceptions in only the appropriate layers, without having annoying
boilerplate catch-and-throw blocks and exception declarations in your DAOs.
这允许您仅在适当的层处理大多数不可恢复的持久性异常,无需在您的 DAO 中添加烦人的样板捕获和抛出块以及异常声明。
(You can still trap and handle exceptions anywhere you need to though.) As mentioned above, JDBC exceptions (including
database-specific dialects) are also converted to the same hierarchy, meaning that you can perform some operations with
JDBC within a consistent programming model.
(尽管如此,您仍然可以在需要的地方捕获和处理异常。)如上所述,JDBC 异常(包括特定数据库的方言)也被转换为相同的层次结构,这意味着您可以在一致的编程模型中使用
JDBC 执行一些操作。
The preceding discussion holds true for the various template classes in Spring’s support for various ORM frameworks. If
you use the interceptor-based classes, the application must care about handling HibernateExceptions and
PersistenceExceptions itself, preferably by delegating to the convertHibernateAccessException(..) or
convertJpaAccessException(..) methods, respectively, of SessionFactoryUtils. These methods convert the exceptions to
exceptions that are compatible with the exceptions in the org.springframework.dao exception hierarchy. As
PersistenceExceptions are unchecked, they can get thrown, too (sacrificing generic DAO abstraction in terms of
exceptions, though).
前述讨论适用于 Spring 对各种 ORM 框架支持的各个模板类。如果您使用基于拦截器的类,应用程序必须关注处理
HibernateExceptions 和 PersistenceExceptions 本身,最好是通过分别委托给 SessionFactoryUtils 的
convertHibernateAccessException(..) 或 convertJpaAccessException(..) 方法。这些方法将异常转换为与
org.springframework.dao 异常层次结构中的异常兼容的异常。由于 PersistenceExceptions 是不检查的,它们也可以被抛出(尽管这牺牲了在异常方面的通用
DAO 抽象)。
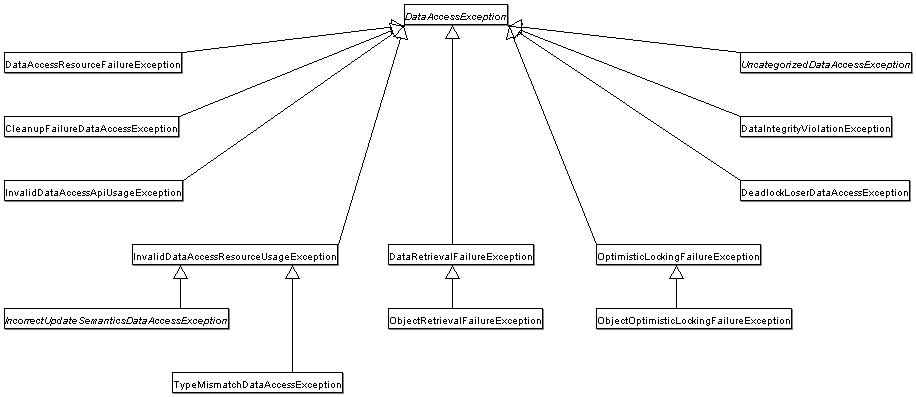
The following image shows the exception hierarchy that Spring provides. (Note that the class hierarchy detailed in the
image shows only a subset of the entire DataAccessException hierarchy.)
以下图像显示了 Spring 提供的异常层次结构。(请注意,图中详细显示的类层次结构仅显示了整个 DataAccessException 层次结构的一个子集。)
(#dao-annotations)2.2. Annotations Used to Configure DAO or Repository Classes
2.2. 用于配置 DAO 或仓库类的注释
The best way to guarantee that your Data Access Objects (DAOs) or repositories provide exception translation is to use
the @Repository annotation. This annotation also lets the component scanning support find and configure your DAOs and
repositories without having to provide XML configuration entries for them. The following example shows how to use the
@Repository annotation:
最佳保证您的数据访问对象(DAOs)或存储库提供异常翻译的方法是使用 @Repository 注解。此注解还允许组件扫描支持查找和配置您的
DAOs 和存储库,而无需为它们提供 XML 配置条目。以下示例展示了如何使用 @Repository 注解:
1
The @Repository annotation.
1
The @Repository annotation.@Repository 注解。
Any DAO or repository implementation needs access to a persistence resource, depending on the persistence technology
used. For example, a JDBC-based repository needs access to a JDBC DataSource, and a JPA-based repository needs access
to an EntityManager. The easiest way to accomplish this is to have this resource dependency injected by using one of
the @Autowired, @Inject, @Resource or @PersistenceContext annotations. The following example works for a JPA
repository:
任何 DAO 或仓库实现都需要访问持久化资源,具体取决于所使用的持久化技术。例如,基于 JDBC 的仓库需要访问 JDBC DataSource
,而基于 JPA 的仓库需要访问 EntityManager 。最简单的方法是通过使用 @Autowired 、 @Inject 、 @Resource 或
@PersistenceContext 之一进行资源依赖注入来实现这一点。以下示例适用于 JPA 仓库:
If you use the classic Hibernate APIs, you can inject SessionFactory, as the following example shows:
如果您使用经典的 Hibernate API,可以注入 SessionFactory ,如下例所示:
The last example we show here is for typical JDBC support. You could have the DataSource injected into an
initialization method or a constructor, where you would create a JdbcTemplate and other data access support classes (
such as SimpleJdbcCall and others) by using this DataSource. The following example autowires a DataSource:
此处展示的最后一个示例是针对典型的 JDBC 支持。您可以将 DataSource 注入到初始化方法或构造函数中,在那里您将创建
JdbcTemplate 和其他数据访问支持类(如 SimpleJdbcCall 等)通过使用此 DataSource 。以下示例自动连接一个 DataSource :
See the specific coverage of each persistence technology for details on how to configure the application context to take
advantage of these annotations.
查看每种持久化技术的具体覆盖范围,以了解如何配置应用程序上下文以利用这些注解的详细信息。