1.1. DispatcherServlet
预计阅读时间: 63 分钟Spring MVC, as many other web frameworks, is designed around the front controller pattern where a central Servlet, the
DispatcherServlet, provides a shared algorithm for request processing, while actual work is performed by configurable
delegate components. This model is flexible and supports diverse workflows.
Spring MVC,与其他许多 Web 框架一样,是基于前端控制器模式设计的,其中中央控制器提供共享的请求处理算法,而实际工作由可配置的代理组件执行。这种模型灵活且支持多样化的工作流程。
The DispatcherServlet, as any Servlet, needs to be declared and mapped according to the Servlet specification by
using Java configuration or in web.xml. In turn, the DispatcherServlet uses Spring configuration to discover the
delegate components it needs for request mapping, view resolution, exception
handling, and more.
DispatcherServlet ,就像任何 Servlet 一样,需要根据 Servlet 规范通过 Java 配置或在 web.xml 中进行声明和映射。反过来,
DispatcherServlet 使用 Spring 配置来发现它需要的代理组件,用于请求映射、视图解析、异常处理等。
The following example of the Java configuration registers and initializes the DispatcherServlet, which is
auto-detected by the Servlet container (see Servlet Config):
以下 Java 配置示例注册并初始化 DispatcherServlet ,该配置由 Servlet 容器自动检测(见 Servlet 配置):
In addition to using the ServletContext API directly, you can also extend
AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer and override specific methods (see the example
under Context Hierarchy).
除了直接使用 ServletContext API 之外,还可以扩展 AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer 并重写特定方法(请参阅
Context Hierarchy 下的示例)。
For programmatic use cases, a GenericWebApplicationContext can be used as an alternative to
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext. See the
GenericWebApplicationContext
javadoc for details.
对于程序化用例,可以使用 GenericWebApplicationContext 作为 AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext 的替代。请参阅
GenericWebApplicationContext javadoc 获取详细信息。
The following example of web.xml configuration registers and initializes the DispatcherServlet:
以下示例中的 web.xml 配置注册并初始化了 DispatcherServlet :
Spring Boot follows a different initialization sequence. Rather than hooking into the lifecycle of the Servlet
container, Spring Boot uses Spring configuration to bootstrap itself and the embedded Servlet container. Filter and
Servlet declarations are detected in Spring configuration and registered with the Servlet container. For more details,
see
the Spring Boot documentation.
Spring Boot 遵循不同的初始化顺序。它不是通过挂钩 Servlet 容器的生命周期,而是使用 Spring 配置来自举和嵌入的 Servlet 容器。在
Spring 配置中检测到 Filter 和 Servlet 声明,并将其注册到 Servlet 容器中。有关更多详细信息,请参阅 Spring Boot 文档。
(#mvc-servlet-context-hierarchy)1.1.1. Context Hierarchy
1.1.1. 上下文层次
DispatcherServlet expects a WebApplicationContext (an extension of a plain ApplicationContext) for its own
configuration. WebApplicationContext has a link to the ServletContext and the Servlet with which it is associated.
It is also bound to the ServletContext such that applications can use static methods on RequestContextUtils to look
up the WebApplicationContext if they need access to it.
DispatcherServlet 预期一个 WebApplicationContext (一个纯 ApplicationContext 的扩展)来配置自身。
WebApplicationContext 与其关联的 ServletContext 和 Servlet 有链接。它还绑定到 ServletContext ,这样应用程序可以使用
RequestContextUtils 上的静态方法来查找 WebApplicationContext ,如果需要访问它的话。
For many applications, having a single WebApplicationContext is simple and suffices. It is also possible to have a
context hierarchy where one root WebApplicationContext is shared across multiple DispatcherServlet (or other
Servlet) instances, each with its own child WebApplicationContext configuration. See Additional Capabilities of the
ApplicationContext
for more on the context hierarchy feature.
对于许多应用程序来说,只有一个 WebApplicationContext 就足够简单了。也可以有一个上下文层次结构,其中一个根
WebApplicationContext 被多个 DispatcherServlet (或其他 Servlet )实例共享,每个实例都有自己的子
WebApplicationContext 配置。有关上下文层次结构功能的更多信息,请参阅 ApplicationContext 的附加功能。
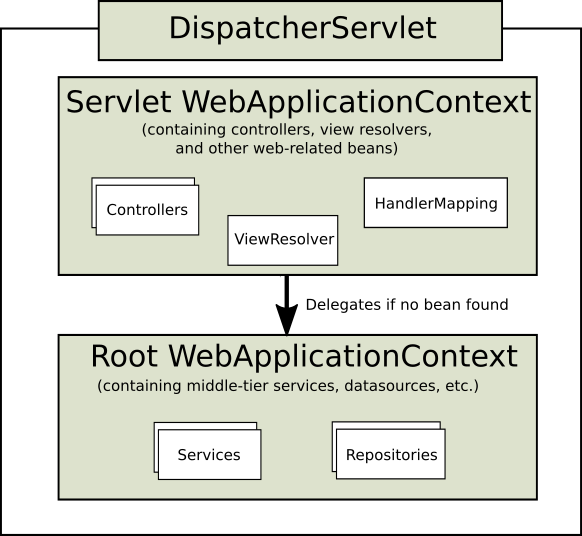
The root WebApplicationContext typically contains infrastructure beans, such as data repositories and business
services that need to be shared across multiple Servlet instances. Those beans are effectively inherited and can be
overridden (that is, re-declared) in the Servlet-specific child WebApplicationContext, which typically contains beans
local to the given Servlet. The following image shows this relationship:
根 WebApplicationContext 通常包含基础设施豆,例如需要跨多个 Servlet 实例共享的数据存储库和业务服务。这些豆被有效地继承,并且可以在
Servlet 特定的子 WebApplicationContext 中覆盖(即重新声明),该子 WebApplicationContext 通常包含给定 Servlet
的本地豆。以下图像显示了这种关系:
The following example configures a WebApplicationContext hierarchy:
以下示例配置了一个 WebApplicationContext 层次结构:
If an application context hierarchy is not required, applications can return all configuration through
getRootConfigClasses() and null from getServletConfigClasses().
如果不需要应用程序上下文层次结构,应用程序可以通过 getRootConfigClasses() 和 null 从 getServletConfigClasses()
返回所有配置。
The following example shows the web.xml equivalent:
以下示例显示了 web.xml 的等效:
If an application context hierarchy is not required, applications may configure a “root” context only and leave the
contextConfigLocation Servlet parameter empty.
如果不需要应用程序上下文层次结构,应用程序可以仅配置一个“根”上下文,并将 contextConfigLocation Servlet 参数留空。
(#mvc-servlet-special-bean-types)1.1.2. Special Bean Types
1.1.2. 特殊 Bean 类型
The DispatcherServlet delegates to special beans to process requests and render the appropriate responses. By “special
beans” we mean Spring-managed Object instances that implement framework contracts. Those usually come with built-in
contracts, but you can customize their properties and extend or replace them.
The DispatcherServlet delegates to special beans to process requests and render the appropriate responses. By “special
beans” we mean Spring-managed Object instances that implement framework contracts. Those usually come with built-in
contracts, but you can customize their properties and extend or replace them. DispatcherServlet
将任务委托给特殊豆来处理请求并生成适当的响应。我们所说的“特殊豆”是指实现框架契约的 Spring 管理的Object
实例。这些通常带有内置契约,但您可以自定义它们的属性,并扩展或替换它们。
The following table lists the special beans detected by the DispatcherServlet:
以下表格列出了由 DispatcherServlet 检测到的特殊 Bean
Bean type Bean 类型
Explanation 说明
HandlerMapping
Map a request to a handler along with a list of interceptors for pre- and
post-processing. The mapping is based on some criteria, the details of which vary by HandlerMapping implementation.
将请求映射到处理器,并附带预处理和后处理的拦截器列表。映射基于某些标准,其细节因实现而异。
The two main HandlerMapping implementations are RequestMappingHandlerMapping (which supports @RequestMapping
annotated methods) and SimpleUrlHandlerMapping (which maintains explicit registrations of URI path patterns to
handlers).
两个主要实现是 RequestMappingHandlerMapping (支持 @RequestMapping 注解方法)和 SimpleUrlHandlerMapping (显式注册
URI 路径模式到处理器)。
HandlerAdapter
Help the DispatcherServlet to invoke a handler mapped to a request, regardless of how the handler is actually invoked.
For example, invoking an annotated controller requires resolving annotations. The main purpose of a HandlerAdapter is
to shield the DispatcherServlet from such details.
帮助 DispatcherServlet 调用映射到请求的处理程序,无论处理程序实际上是如何被调用的。例如,调用注解控制器需要解析注解。
HandlerAdapter 的主要目的是保护 DispatcherServlet 不受这些细节的影响。
Strategy to resolve exceptions, possibly mapping them to handlers, to HTML error views, or other targets.
See Exceptions.
异常解决策略,可能将它们映射到处理器、HTML 错误视图或其他目标。见异常。
Resolve logical String-based view names returned from a handler to an actual View with which to render to the
response. See View Resolution and View Technologies.
解析由处理器返回的逻辑 String 视图名称,将其转换为实际 View 以用于渲染到响应中。请参阅视图解析和视图技术。
LocaleResolver, LocaleContextResolver
LocaleResolver ,LocaleContextResolver
Resolve the Locale a client is using and possibly their time zone, in order to be able to offer internationalized
views. See Locale.
解决客户端使用的 Locale 以及可能的时间区域,以便能够提供国际化视图。参见 Locale。
Resolve themes your web application can use — for example, to offer personalized layouts.
See Themes.
解决您的 Web 应用程序可以使用的主题 - 例如,提供个性化布局。参见主题。
Abstraction for parsing a multi-part request (for example, browser form file upload) with the help of some multipart
parsing library. See Multipart Resolver.
抽象化多部分请求(例如,浏览器表单文件上传)的解析,借助某些多部分解析库。参见多部分解析器。
Store and retrieve the “input” and the “output” FlashMap that can be used to pass attributes from one request to
another, usually across a redirect. See Flash Attributes.
存储和检索“输入”和“输出” FlashMap ,这些可以用于从一个请求传递到另一个请求,通常是在重定向过程中。参见 Flash 属性。
(#mvc-servlet-config)1.1.3. Web MVC Config
1.1.3. Web MVC 配置
Applications can declare the infrastructure beans listed in Special Bean Types that
are required to process requests. The DispatcherServlet checks the WebApplicationContext for each special bean. If
there are no matching bean types, it falls back on the default types listed in
DispatcherServlet.properties.
应用程序可以声明在特殊 Bean 类型中列出的基础设施 Bean,这些 Bean 是处理请求所必需的。 DispatcherServlet 检查每个特殊
Bean 的 WebApplicationContext 。如果没有匹配的 Bean 类型,它将回退到 DispatcherServlet.properties 中列出的默认类型。
In most cases, the MVC Config is the best starting point. It declares the required beans in either Java
or XML and provides a higher-level configuration callback API to customize it.
在大多数情况下,MVC 配置是最好的起点。它声明所需的 beans,无论是 Java 还是 XML,并提供高级配置回调 API 以进行自定义。
Spring Boot relies on the MVC Java configuration to configure Spring MVC and provides many extra convenient options.
Spring Boot 依赖于 MVC Java 配置来配置 Spring MVC,并提供了许多额外的便捷选项。
(#mvc-container-config)1.1.4. Servlet Config 1.1.4. Servlet 配置
In a Servlet 3.0+ environment, you have the option of configuring the Servlet container programmatically as an
alternative or in combination with a web.xml file. The following example registers a DispatcherServlet:
在 Servlet 3.0+环境中,您可以选择以编程方式配置 Servlet 容器,作为 web.xml 文件的替代方案或与之结合。以下示例注册了一个
DispatcherServlet :
WebApplicationInitializer is an interface provided by Spring MVC that ensures your implementation is detected and
automatically used to initialize any Servlet 3 container. An abstract base class implementation of
WebApplicationInitializer named AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer makes it even easier to register the
DispatcherServlet by overriding methods to specify the servlet mapping and the location of the DispatcherServlet
configuration.
WebApplicationInitializer 是 Spring MVC 提供的一个接口,确保您的实现被检测并自动用于初始化任何 Servlet 3 容器。名为
WebApplicationInitializer 的抽象基类实现 AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer 使得通过覆盖方法来指定 servlet 映射和
DispatcherServlet 配置的位置,从而更容易注册 DispatcherServlet 。
This is recommended for applications that use Java-based Spring configuration, as the following example shows:
这是推荐用于使用基于 Java 的 Spring 配置的应用程序,如下例所示:
If you use XML-based Spring configuration, you should extend directly from AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer, as
the following example shows:
如果您使用基于 XML 的 Spring 配置,应直接从 AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer 扩展,如下例所示:
AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer also provides a convenient way to add Filter instances and have them be
automatically mapped to the DispatcherServlet, as the following example shows:
AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer 还提供了一种方便的方法来添加 Filter 实例,并自动将它们映射到 DispatcherServlet
,如下例所示:
Each filter is added with a default name based on its concrete type and automatically mapped to the
DispatcherServlet.
每个过滤器都根据其实际类型添加一个默认名称,并自动映射到 DispatcherServlet 。
The isAsyncSupported protected method of AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer provides a single place to enable
async support on the DispatcherServlet and all filters mapped to it. By default, this flag is set to true.
isAsyncSupported 的受保护方法提供了一个单独的位置来启用 DispatcherServlet 及其所有映射的过滤器上的异步支持。默认情况下,此标志设置为
true 。
Finally, if you need to further customize the DispatcherServlet itself, you can override the createDispatcherServlet
method.
最后,如果您需要进一步自定义 DispatcherServlet 本身,您可以重写 createDispatcherServlet 方法。
(#mvc-servlet-sequence)1.1.5. Processing 1.1.5. 处理
The DispatcherServlet processes requests as follows:
The DispatcherServlet processes requests as follows: 该DispatcherServlet按照以下方式处理请求:
-
The
WebApplicationContextis searched for and bound in the request as an attribute that the controller and other elements in the process can use. It is bound by default under theDispatcherServlet.WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTEkey.
WebApplicationContext在请求中搜索并绑定为一个控制器和其他流程元素可以使用的属性。它默认绑定在DispatcherServlet.WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE键下。 -
The locale resolver is bound to the request to let elements in the process resolve the locale to use when processing the request (rendering the view, preparing data, and so on). If you do not need locale resolving, you do not need the locale resolver.
区域解析器绑定到请求,以便在处理请求(渲染视图、准备数据等)时,元素可以解析要使用的区域。如果您不需要区域解析,则不需要区域解析器。 -
The theme resolver is bound to the request to let elements such as views determine which theme to use. If you do not use themes, you can ignore it.
主题解析器绑定到请求,以便元素如视图确定使用哪个主题。如果您不使用主题,可以忽略它。 -
If you specify a multipart file resolver, the request is inspected for multiparts. If multiparts are found, the request is wrapped in a
MultipartHttpServletRequestfor further processing by other elements in the process. See Multipart Resolver for further information about multipart handling.
如果您指定了多部分文件解析器,则请求将检查是否存在多部分。如果找到多部分,则请求将包装在MultipartHttpServletRequest中以供过程中其他元素进一步处理。有关多部分处理的更多信息,请参阅多部分解析器。 -
An appropriate handler is searched for. If a handler is found, the execution chain associated with the handler ( preprocessors, postprocessors, and controllers) is run to prepare a model for rendering.
一个合适的处理器正在被搜索。如果找到一个处理器,将运行与该处理器关联的执行链(预处理程序、后处理程序和控制器),以准备一个用于渲染的模型。
Alternatively, for annotated controllers, the response can be rendered (within theHandlerAdapter) instead of returning a view.
或者,对于注解控制器,可以在(HandlerAdapter)内渲染响应,而不是返回视图。 -
If a model is returned, the view is rendered. If no model is returned (maybe due to a preprocessor or postprocessor intercepting the request, perhaps for security reasons), no view is rendered, because the request could already have been fulfilled.
如果返回了一个模型,则渲染视图。如果没有返回模型(可能是因为预处理程序或后处理程序拦截了请求,可能是出于安全原因),则不渲染视图,因为请求可能已经得到满足。
The HandlerExceptionResolver beans declared in the WebApplicationContext are used to resolve exceptions thrown
during request processing. Those exception resolvers allow customizing the logic to address exceptions.
See Exceptions for more details.
在 WebApplicationContext 中声明的 HandlerExceptionResolver beans 用于解决请求处理过程中抛出的异常。这些异常解析器允许自定义处理异常的逻辑。有关详细信息,请参阅异常。
For HTTP caching support, handlers can use the checkNotModified methods of WebRequest, along with further options
for annotated controllers as described in HTTP Caching for Controllers.
为了 HTTP 缓存支持,处理器可以使用 WebRequest 的 checkNotModified 方法,以及如 HTTP Caching for Controllers
中所述的注解控制器进一步选项。
You can customize individual DispatcherServlet instances by adding Servlet initialization parameters (init-param
elements) to the Servlet declaration in the web.xml file. The following table lists the supported parameters:
您可以通过在 web.xml 文件中 Servlet 声明中添加 Servlet 初始化参数( init-param 元素)来自定义单个 DispatcherServlet
实例。以下表格列出了支持的参数:
Table 1. DispatcherServlet initialization parameters
表 1. DispatcherServlet 初始化参数
Parameter 参数
Explanation 说明
contextClass
Class that implements ConfigurableWebApplicationContext, to be instantiated and locally configured by this Servlet. By
default, XmlWebApplicationContext is used.
类实现 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext ,由该 Servlet 实例化和本地配置。默认情况下,使用 XmlWebApplicationContext 。
contextConfigLocation
String that is passed to the context instance (specified by contextClass) to indicate where contexts can be found. The
string consists potentially of multiple strings (using a comma as a delimiter) to support multiple contexts. In the case
of multiple context locations with beans that are defined twice, the latest location takes precedence.
字符串传递给上下文实例(由 contextClass 指定)以指示上下文可以找到的位置。该字符串可能由多个字符串(使用逗号作为分隔符)组成,以支持多个上下文。在存在定义两次的
bean 的多个上下文位置的情况下,最新位置具有优先权。
namespace
Namespace of the WebApplicationContext. Defaults to [servlet-name]-servlet.
命名空间为 WebApplicationContext 。默认为 [servlet-name]-servlet 。
throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound
Whether to throw a NoHandlerFoundException when no handler was found for a request. The exception can then be caught
with a HandlerExceptionResolver (for example, by using an @ExceptionHandler controller method) and handled as any
others.
是否抛出 NoHandlerFoundException 当没有找到请求的处理程序时。然后可以使用 HandlerExceptionResolver (例如,通过使用
@ExceptionHandler 控制器方法)捕获异常,并像处理其他异常一样处理。
By default, this is set to false, in which case the DispatcherServlet sets the response status to 404 (NOT_FOUND)
without raising an exception.
默认情况下,这设置为 false ,在这种情况下, DispatcherServlet 将响应状态设置为 404(NOT_FOUND),而不会抛出异常。
Note that, if default servlet handling is also configured, unresolved requests are
always forwarded to the default servlet and a 404 is never raised.
请注意,如果也配置了默认 Servlet 处理,则未解决的请求始终转发到默认 Servlet,永远不会引发 404 错误。
(#mvc-handlermapping-path)1.1.6. Path Matching 1.1.6. 路径匹配
The Servlet API exposes the full request path as requestURI and further sub-divides it into contextPath,
servletPath, and pathInfo whose values vary depending on how a Servlet is mapped. From these inputs, Spring MVC
needs to determine the lookup path to use for handler mapping, which is the path within the mapping of the
DispatcherServlet itself, excluding the contextPath and any servletMapping prefix, if present.
Servlet API 公开了完整的请求路径作为 requestURI ,并将其进一步细分为 contextPath 、 servletPath 和 pathInfo
,这些值取决于 Servlet 的映射方式。从这些输入中,Spring MVC 需要确定用于处理器映射的查找路径,即 DispatcherServlet
映射内的路径,不包括 contextPath 以及任何存在的 servletMapping 前缀。
The servletPath and pathInfo are decoded and that makes them impossible to compare directly to the full requestURI
in order to derive the lookupPath and that makes it necessary to decode the requestURI. However this introduces its
own issues because the path may contain encoded reserved characters such as "/" or ";" that can in turn alter the
structure of the path after they are decoded which can also lead to security issues. In addition, Servlet containers may
normalize the servletPath to varying degrees which makes it further impossible to perform startsWith comparisons
against the requestURI.
servletPath 和 pathInfo 被解码,这使得它们无法直接与完整的 requestURI 进行比较以推导出 lookupPath,因此有必要解码
requestURI 。然而,这引入了自己的问题,因为路径可能包含编码的保留字符,如 "/" 或 ";"
,这些字符在解码后可能会改变路径的结构,从而导致安全问题。此外,Servlet 容器可能会以不同的程度对 servletPath 进行规范化,这使得对
requestURI 进行 startsWith 比较变得更加不可能。
This is why it is best to avoid reliance on the servletPath which comes with the prefix-based servletPath mapping
type. If the DispatcherServlet is mapped as the default Servlet with "/" or otherwise without a prefix with "/*"
and the Servlet container is 4.0+ then Spring MVC is able to detect the Servlet mapping type and avoid use of the
servletPath and pathInfo altogether. On a 3.1 Servlet container, assuming the same Servlet mapping types, the
equivalent can be achieved by providing a UrlPathHelper with alwaysUseFullPath=true
via Path Matching in the MVC config.
这是为什么最好避免依赖于带有前缀映射类型的 servletPath 。如果 DispatcherServlet 被映射为默认 Servlet,使用 "/"
或没有前缀的 "/*" ,并且 Servlet 容器是 4.0+,那么 Spring MVC 能够检测 Servlet 映射类型并完全避免使用 servletPath 和
pathInfo 。在 3.1 Servlet 容器上,假设相同的 Servlet 映射类型,可以通过在 MVC 配置中提供带有 alwaysUseFullPath=true 的
UrlPathHelper 通过路径匹配来实现等效功能。
Fortunately the default Servlet mapping "/" is a good choice. However, there is still an issue in that the
requestURI needs to be decoded to make it possible to compare to controller mappings. This is again undesirable
because of the potential to decode reserved characters that alter the path structure.
幸运的是,默认的 Servlet 映射 "/" 是一个不错的选择。然而,仍然存在一个问题,即 requestURI
需要解码才能与控制器映射进行比较。这又是不理想的,因为解码可能会改变路径结构的保留字符。
If such characters are not expected, then you can reject them (like the Spring Security HTTP firewall), or you can
configure UrlPathHelper with urlDecode=false but controller mappings will need to match to the encoded path which
may not always work well. Furthermore, sometimes the DispatcherServlet needs to share the URL space with another
Servlet and may need to be mapped by prefix.
如果预期不到这些字符,则可以拒绝它们(例如 Spring Security HTTP 防火墙),或者您可以将 UrlPathHelper 配置为
urlDecode=false ,但控制器映射需要匹配到编码后的路径,这可能并不总是工作得很好。此外,有时 DispatcherServlet 需要与另一个
Servlet 共享 URL 空间,可能需要通过前缀进行映射。
The above issues can be addressed more comprehensively by switching from PathMatcher to the parsed PathPattern
available in 5.3 or higher, see Pattern Comparison. Unlike
AntPathMatcher which needs either the lookup path decoded or the controller mapping encoded, a parsed PathPattern
matches to a parsed representation of the path called RequestPath, one path segment at a time. This allows decoding
and sanitizing path segment values individually without the risk of altering the structure of the path. Parsed
PathPattern also supports the use of servletPath prefix mapping as long as the prefix is kept simple and does not
have any characters that need to be encoded.
上述问题可以通过从 PathMatcher 切换到 5.3 或更高版本中可用的解析后的 PathPattern 来更全面地解决,参见模式比较。与需要解码查找路径或编码控制器映射的
AntPathMatcher 不同,解析后的 PathPattern 与路径的解析表示 RequestPath 匹配,一次一个路径段。这允许单独解码和清理路径段值,而不会改变路径的结构。解析后的
PathPattern 还支持使用 servletPath 前缀映射,只要前缀保持简单且不包含任何需要编码的字符。
(#mvc-handlermapping-interceptor)1.1.7. Interception 1.1.7. 拦截
All HandlerMapping implementations support handler interceptors that are useful when you want to apply specific
functionality to certain requests — for example, checking for a principal. Interceptors must implement
HandlerInterceptor from the org.springframework.web.servlet package with three methods that should provide enough
flexibility to do all kinds of pre-processing and post-processing:
所有 HandlerMapping 实现都支持处理拦截器,这在您想对某些请求应用特定功能时很有用——例如,检查主体。拦截器必须实现来自
org.springframework.web.servlet 包的 HandlerInterceptor ,包含三个方法,这些方法应该提供足够的灵活性来完成各种预处理和后处理:
-
preHandle(..): Before the actual handler is run
preHandle(..): 在实际处理器运行之前 -
postHandle(..): After the handler is run
postHandle(..): 处理器运行后 -
afterCompletion(..): After the complete request has finished
afterCompletion(..): 完成请求后
The preHandle(..) method returns a boolean value. You can use this method to break or continue the processing of the
execution chain. When this method returns true, the handler execution chain continues. When it returns false, the
DispatcherServlet assumes the interceptor itself has taken care of requests (and, for example, rendered an appropriate
view) and does not continue executing the other interceptors and the actual handler in the execution chain.
该方法返回一个布尔值。您可以使用此方法来中断或继续执行链的处理。当此方法返回 true 时,处理器执行链继续。当它返回 false 时,
DispatcherServlet 假定拦截器本身已处理请求(例如,渲染适当的视图)并且不会继续执行执行链中的其他拦截器和实际处理器。
See Interceptors in the section on MVC configuration for examples of how to configure
interceptors. You can also register them directly by using setters on individual HandlerMapping implementations.
查看 MVC 配置部分中的拦截器示例,了解如何配置拦截器。您还可以通过使用单个 HandlerMapping 实现上的 setter 直接注册它们。
postHandle method is less useful with @ResponseBody and ResponseEntity methods for which the response is written
and committed within the HandlerAdapter and before postHandle. That means it is too late to make any changes to the
response, such as adding an extra header. For such scenarios, you can implement ResponseBodyAdvice and either declare
it as an Controller Advice bean or configure it directly on
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.
postHandle 方法在 @ResponseBody 和 ResponseEntity 方法中不太有用,因为这些方法在 HandlerAdapter 和 postHandle
之前写入并提交了响应。这意味着更改响应(如添加额外的头信息)已经太晚了。对于此类场景,您可以实现 ResponseBodyAdvice ,并将其声明为
Controller Advice bean 或直接在 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 上配置。
(#mvc-exceptionhandlers)1.1.8. Exceptions 1.1.8. 异常
If an exception occurs during request mapping or is thrown from a request handler (such as a @Controller), the
DispatcherServlet delegates to a chain of HandlerExceptionResolver beans to resolve the exception and provide
alternative handling, which is typically an error response.
如果在请求映射过程中发生异常或由请求处理器(如 @Controller )抛出, DispatcherServlet 将委托给一系列
HandlerExceptionResolver 豆类来处理异常并提供替代处理,这通常是错误响应。
The following table lists the available HandlerExceptionResolver implementations:
以下表格列出了可用的 HandlerExceptionResolver 实现:
Table 2. HandlerExceptionResolver implementations
表 2. HandlerExceptionResolver 实现
HandlerExceptionResolver
Description 描述
SimpleMappingExceptionResolver
A mapping between exception class names and error view names. Useful for rendering error pages in a browser
application.
异常类名称与错误视图名称之间的映射。用于在浏览器应用程序中渲染错误页面。
DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
Resolves exceptions raised by Spring MVC and maps them to HTTP status codes. See also alternative
ResponseEntityExceptionHandler and REST API exceptions.
解决 Spring MVC 抛出的异常并将它们映射到 HTTP 状态码。另见替代 ResponseEntityExceptionHandler 和 REST API 异常。
ResponseStatusExceptionResolver
Resolves exceptions with the @ResponseStatus annotation and maps them to HTTP status codes based on the value in the
annotation.
解决由 @ResponseStatus 注解引发的异常,并根据注解中的值将它们映射到 HTTP 状态码。
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver
Resolves exceptions by invoking an @ExceptionHandler method in a @Controller or a @ControllerAdvice class.
See @ExceptionHandler methods.
通过调用一个 @Controller 或 @ControllerAdvice 类中的 @ExceptionHandler 方法来解决异常。请参阅 @ExceptionHandler 方法。
(#mvc-exceptionhandlers-handling)Chain of Resolvers 解析链
You can form an exception resolver chain by declaring multiple HandlerExceptionResolver beans in your Spring
configuration and setting their order properties as needed. The higher the order property, the later the exception
resolver is positioned.
您可以通过在 Spring 配置中声明多个 HandlerExceptionResolver bean 并设置它们的 order 属性来形成异常解析器链。属性值越高,异常解析器的位置就越靠后。
The contract of HandlerExceptionResolver specifies that it can return:
《 HandlerExceptionResolver 》的合同规定它可以返回:
-
a
ModelAndViewthat points to an error view.
一个指向错误视图的ModelAndView。 -
An empty
ModelAndViewif the exception was handled within the resolver.
如果异常在解析器内部被处理,则为空ModelAndView。 -
nullif the exception remains unresolved, for subsequent resolvers to try, and, if the exception remains at the end, it is allowed to bubble up to the Servlet container.
如果异常仍然未解决,则供后续解析器尝试解决,如果异常最终仍未解决,则允许它向上冒泡到 Servlet 容器。
The MVC Config automatically declares built-in resolvers for default Spring MVC exceptions, for
@ResponseStatus annotated exceptions, and for support of @ExceptionHandler methods. You can customize that list or
replace it.
MVC 配置自动声明了默认 Spring MVC 异常的内置解析器,用于 @ResponseStatus 注解的异常,以及支持 @ExceptionHandler
方法。您可以自定义该列表或替换它。
(#mvc-ann-customer-servlet-container-error-page)Container Error Page 容器错误页面
If an exception remains unresolved by any HandlerExceptionResolver and is, therefore, left to propagate or if the
response status is set to an error status (that is, 4xx, 5xx), Servlet containers can render a default error page in
HTML. To customize the default error page of the container, you can declare an error page mapping in web.xml. The
following example shows how to do so:
如果任何 HandlerExceptionResolver 无法解决异常,因此异常被传播,或者如果响应状态被设置为错误状态(即 4xx、5xx),Servlet
容器可以以 HTML 形式渲染默认错误页面。要自定义容器的默认错误页面,您可以在 web.xml 中声明错误页面映射。以下示例展示了如何操作:
Given the preceding example, when an exception bubbles up or the response has an error status, the Servlet container
makes an ERROR dispatch within the container to the configured URL (for example, /error). This is then processed by
the DispatcherServlet, possibly mapping it to a @Controller, which could be implemented to return an error view name
with a model or to render a JSON response, as the following example shows:
根据前面的示例,当异常向上冒泡或响应状态有错误时,Servlet 容器会在容器内将 ERROR 分派到配置的 URL(例如, /error )。然后由
DispatcherServlet 处理,可能将其映射到 @Controller ,这可以实现返回带有模型的错误视图名称或渲染 JSON 响应,如下例所示:
The Servlet API does not provide a way to create error page mappings in Java. You can, however, use both a
WebApplicationInitializer and a minimal web.xml.
Servlet API 不提供在 Java 中创建错误页面映射的方法。然而,您可以使用 WebApplicationInitializer 和最小 web.xml 。
(#mvc-viewresolver)1.1.9. View Resolution 1.1.9. 视图分辨率
Spring MVC defines the ViewResolver and View interfaces that let you render models in a browser without tying you to
a specific view technology. ViewResolver provides a mapping between view names and actual views. View addresses the
preparation of data before handing over to a specific view technology.
Spring MVC 定义了 ViewResolver 和 View 接口,允许您在浏览器中渲染模型,而不必绑定到特定的视图技术。 ViewResolver
提供了视图名称和实际视图之间的映射。 View 解决了在传递给特定视图技术之前准备数据的问题。
The following table provides more details on the ViewResolver hierarchy:
以下表格提供了关于 ViewResolver 层级的更多详细信息:
Table 3. ViewResolver implementations
表 3. 视图解析器实现
ViewResolver 视图解析器
Description 描述
AbstractCachingViewResolver
Subclasses of AbstractCachingViewResolver cache view instances that they resolve. Caching improves performance of
certain view technologies. You can turn off the cache by setting the cache property to false. Furthermore, if you
must refresh a certain view at runtime (for example, when a FreeMarker template is modified), you can use the
removeFromCache(String viewName, Locale loc) method.
子类缓存它们解析的视图实例。缓存可以提高某些视图技术的性能。您可以通过设置 cache 属性为 false
来关闭缓存。此外,如果您必须在运行时刷新某个视图(例如,当 FreeMarker 模板被修改时),您可以使用
removeFromCache(String viewName, Locale loc) 方法。
UrlBasedViewResolver
Simple implementation of the ViewResolver interface that effects the direct resolution of logical view names to URLs
without an explicit mapping definition. This is appropriate if your logical names match the names of your view resources
in a straightforward manner, without the need for arbitrary mappings.
简单实现 ViewResolver 接口,该接口直接将逻辑视图名称解析为 URL,无需显式映射定义。如果您的逻辑名称与视图资源名称直接对应,无需任意映射,则适用。
InternalResourceViewResolver
Convenient subclass of UrlBasedViewResolver that supports InternalResourceView (in effect, Servlets and JSPs) and
subclasses such as JstlView and TilesView. You can specify the view class for all views generated by this resolver
by using setViewClass(..). See the
UrlBasedViewResolver
javadoc for details.
方便的 UrlBasedViewResolver 子类,支持 InternalResourceView (实际上,Servlets 和 JSPs)以及 JstlView 和 TilesView
等子类。您可以通过使用 setViewClass(..) 来指定由该解析器生成的所有视图的视图类。有关详细信息,请参阅
UrlBasedViewResolver javadoc。
FreeMarkerViewResolver
Convenient subclass of UrlBasedViewResolver that supports FreeMarkerView and custom subclasses of them.
方便的 UrlBasedViewResolver 的子类,支持 FreeMarkerView 及其自定义子类。
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver
Implementation of the ViewResolver interface that resolves a view based on the request file name or Accept header.
See Content Negotiation.
实现基于请求文件名或 Accept 头解析视图的 ViewResolver 接口。参见内容协商。
BeanNameViewResolver
Implementation of the ViewResolver interface that interprets a view name as a bean name in the current application
context. This is a very flexible variant which allows for mixing and matching different view types based on distinct
view names. Each such View can be defined as a bean e.g. in XML or in configuration classes.
实现将视图名称解释为当前应用程序上下文中的 bean 名称的 ViewResolver 接口。这是一个非常灵活的变体,允许根据不同的视图名称混合和匹配不同的视图类型。每个这样的
View 都可以定义为 bean,例如在 XML 或配置类中。
(#mvc-viewresolver-handling)Handling 处理
You can chain view resolvers by declaring more than one resolver bean and, if necessary, by setting the order property
to specify ordering. Remember, the higher the order property, the later the view resolver is positioned in the chain.
您可以通过声明多个解析器 bean 来链式配置视图解析器,并在必要时设置 order 属性以指定顺序。请记住,顺序属性值越高,视图解析器在链中的位置就越靠后。
The contract of a ViewResolver specifies that it can return null to indicate that the view could not be found.
However, in the case of JSPs and InternalResourceViewResolver, the only way to figure out if a JSP exists is to
perform a dispatch through RequestDispatcher. Therefore, you must always configure an InternalResourceViewResolver
to be last in the overall order of view resolvers.
合同中指定了 ViewResolver 可以返回 null 以指示视图未找到。然而,在 JSP 和 InternalResourceViewResolver 的情况下,确定
JSP 是否存在唯一的方法是通过 RequestDispatcher 进行调度。因此,您必须始终将 InternalResourceViewResolver
配置为视图解析器整体顺序中的最后一个。
Configuring view resolution is as simple as adding ViewResolver beans to your Spring configuration.
The MVC Config provides a dedicated configuration API for View Resolvers
and for adding logic-less View Controllers which are useful for HTML template rendering
without controller logic.
配置视图分辨率就像在 Spring 配置中添加 ViewResolver beans 一样简单。MVC 配置为视图解析器和添加无逻辑视图控制器提供了专门的配置
API,这对于无控制器逻辑的 HTML 模板渲染非常有用。
(#mvc-redirecting-redirect-prefix)Redirecting 重定向
The special redirect: prefix in a view name lets you perform a redirect. The UrlBasedViewResolver (and its
subclasses) recognize this as an instruction that a redirect is needed. The rest of the view name is the redirect URL.
视图名称中的特殊 redirect: 前缀允许您执行重定向。 UrlBasedViewResolver (及其子类)将其识别为需要重定向的指令。视图名称的其余部分是重定向的
URL。
The net effect is the same as if the controller had returned a RedirectView, but now the controller itself can operate
in terms of logical view names. A logical view name (such as redirect:/myapp/some/resource) redirects relative to the
current Servlet context, while a name such as redirect:https://myhost.com/some/arbitrary/path redirects to an absolute
URL.
网络效果等同于控制器返回了 RedirectView ,但现在控制器本身可以在逻辑视图名称的术语下操作。一个逻辑视图名称(如
redirect:/myapp/some/resource )相对于当前 Servlet 上下文进行重定向,而像
redirect:https://myhost.com/some/arbitrary/path 这样的名称则重定向到绝对 URL。
Note that, if a controller method is annotated with the @ResponseStatus, the annotation value takes precedence over
the response status set by RedirectView.
请注意,如果控制器方法被标注为 @ResponseStatus ,则该注解的值将优先于由 RedirectView 设置的响应状态。
(#mvc-redirecting-forward-prefix)Forwarding 转发
You can also use a special forward: prefix for view names that are ultimately resolved by UrlBasedViewResolver and
subclasses. This creates an InternalResourceView, which does a RequestDispatcher.forward(). Therefore, this prefix
is not useful with InternalResourceViewResolver and InternalResourceView (for JSPs), but it can be helpful if you
use another view technology but still want to force a forward of a resource to be handled by the Servlet/JSP engine.
Note that you may also chain multiple view resolvers, instead.
您还可以使用特殊的 forward: 前缀来表示最终由 UrlBasedViewResolver 及其子类解析的视图名称。这创建了一个
InternalResourceView ,它执行 RequestDispatcher.forward() 。因此,这个前缀在 InternalResourceViewResolver 和
InternalResourceView (对于 JSP)中并不有用,但如果您使用其他视图技术但仍然想强制将资源转发由 Servlet/JSP
引擎处理,则可能很有帮助。请注意,您也可以链接多个视图解析器。
(#mvc-multiple-representations)Content Negotiation 内容协商
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver
does not resolve views itself but rather delegates to other view resolvers and selects the view that resembles the
representation requested by the client. The representation can be determined from the Accept header or from a query
parameter (for example, "/path?format=pdf").
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 不自行解析视图,而是委托给其他视图解析器,并选择与客户端请求的表示相似的视图。表示可以从
Accept 标头或查询参数(例如, "/path?format=pdf" )中确定。
The ContentNegotiatingViewResolver selects an appropriate View to handle the request by comparing the request media
types with the media type (also known as Content-Type) supported by the View associated with each of its
ViewResolvers. The first View in the list that has a compatible Content-Type returns the representation to the
client. If a compatible view cannot be supplied by the ViewResolver chain, the list of views specified through the
DefaultViews property is consulted. This latter option is appropriate for singleton Views that can render an
appropriate representation of the current resource regardless of the logical view name. The Accept header can include
wildcards (for example text/*), in which case a View whose Content-Type is text/xml is a compatible match.
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 选择一个合适的 View 来处理请求,通过比较请求的媒体类型与每个 ViewResolvers 关联的
View 支持的媒体类型(也称为 Content-Type )。列表中第一个具有兼容 Content-Type 的 View 将表示返回给客户端。如果视图链
ViewResolver 无法提供兼容视图,则将咨询通过 DefaultViews 属性指定的视图列表。这种后一种选项适用于可以渲染当前资源适当表示的单例
Views ,无论逻辑视图名称如何。 Accept 头可以包含通配符(例如 text/* ),在这种情况下,一个 View 的 Content-Type 是
text/xml 的兼容匹配。
See View Resolvers under MVC Config for configuration details.
查看 MVC 配置下的视图解析器以获取配置详情。
(#mvc-localeresolver)1.1.10. Locale 1.1.10. 区域设置
Most parts of Spring’s architecture support internationalization, as the Spring web MVC framework does.
DispatcherServlet lets you automatically resolve messages by using the client’s locale. This is done with
LocaleResolver objects.
Spring 架构的大部分组件支持国际化,正如 Spring Web MVC 框架所做的那样。 DispatcherServlet 允许您通过使用客户端的区域设置自动解析消息。这是通过
LocaleResolver 对象完成的。
When a request comes in, the DispatcherServlet looks for a locale resolver and, if it finds one, it tries to use it to
set the locale. By using the RequestContext.getLocale() method, you can always retrieve the locale that was resolved
by the locale resolver.
当请求到来时, DispatcherServlet 寻找一个区域设置解析器,如果找到了,它会尝试使用它来设置区域设置。通过使用
RequestContext.getLocale() 方法,您可以始终检索由区域设置解析器解析的区域设置。
In addition to automatic locale resolution, you can also attach an interceptor to the handler mapping (
see Interception for more information on handler mapping interceptors) to change the
locale under specific circumstances (for example, based on a parameter in the request).
除了自动区域设置解析外,您还可以将拦截器附加到处理器映射(有关处理器映射拦截器的更多信息,请参阅拦截部分)以在特定情况下更改区域设置(例如,基于请求中的参数)。
Locale resolvers and interceptors are defined in the org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n package and are configured
in your application context in the normal way. The following selection of locale resolvers is included in Spring.
区域解析器和拦截器在 org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n 包中定义,并以常规方式配置在您的应用程序上下文中。Spring
中包含以下区域解析器选择。
(#mvc-timezone)Time Zone 时区
In addition to obtaining the client’s locale, it is often useful to know its time zone. The LocaleContextResolver
interface offers an extension to LocaleResolver that lets resolvers provide a richer LocaleContext, which may
include time zone information.
除了获取客户端的区域设置外,了解其时区通常也很有用。 LocaleContextResolver 接口为 LocaleResolver 提供了一个扩展,允许解析器提供更丰富的
LocaleContext ,这可能包括时区信息。
When available, the user’s TimeZone can be obtained by using the RequestContext.getTimeZone() method. Time zone
information is automatically used by any Date/Time Converter and Formatter objects that are registered with Spring’s
ConversionService.
当可用时,可以通过使用 RequestContext.getTimeZone() 方法获取用户的 TimeZone 。任何注册到 Spring 的 ConversionService
的 Date/Time Converter 和 Formatter 对象将自动使用时区信息。
This locale resolver inspects the accept-language header in the request that was sent by the client (for example, a
web browser). Usually, this header field contains the locale of the client’s operating system. Note that this resolver
does not support time zone information.
此区域解析器检查客户端(例如,网页浏览器)发送的请求中的 accept-language 头。通常,此头字段包含客户端操作系统的区域设置。请注意,此解析器不支持时区信息。
(#mvc-localeresolver-cookie)Cookie Resolver Cookie 解析器
This locale resolver inspects a Cookie that might exist on the client to see if a Locale or TimeZone is specified.
If so, it uses the specified details. By using the properties of this locale resolver, you can specify the name of the
cookie as well as the maximum age. The following example defines a CookieLocaleResolver:
此区域解析器检查客户端可能存在的 Cookie ,以查看是否指定了 Locale 或 TimeZone 。如果是,它将使用指定的详细信息。通过使用此区域解析器的属性,您可以指定
cookie 的名称以及最大年龄。以下示例定义了一个 CookieLocaleResolver :
The following table describes the properties CookieLocaleResolver:
以下表格描述了属性 CookieLocaleResolver :
Table 4. CookieLocaleResolver properties
表 4. CookieLocaleResolver 属性
Property 属性
Default 默认
Description 描述
cookieName
classname + LOCALE 类名 + 区域设置
The name of the cookie
Cookies 的名称
cookieMaxAge
Servlet container default
Servlet 容器默认
The maximum time a cookie persists on the client. If -1 is specified, the cookie will not be persisted. It is
available only until the client shuts down the browser.
客户端 cookie 最大持久时间。如果指定了 -1 ,则 cookie 不会持久化。它仅在客户端关闭浏览器前可用。
cookiePath
/
Limits the visibility of the cookie to a certain part of your site. When cookiePath is specified, the cookie is
visible only to that path and the paths below it.
限制 cookie 的可见性到您网站的一部分。当指定 cookiePath 时,cookie 仅对该路径及其以下路径可见。
(#mvc-localeresolver-session)Session Resolver 会话解析器
The SessionLocaleResolver lets you retrieve Locale and TimeZone from the session that might be associated with the
user’s request. In contrast to CookieLocaleResolver, this strategy stores locally chosen locale settings in the
Servlet container’s HttpSession. As a consequence, those settings are temporary for each session and are, therefore,
lost when each session ends.
SessionLocaleResolver 允许您从与用户请求关联的会话中检索 Locale 和 TimeZone 。与 CookieLocaleResolver
相比,此策略将本地选择的区域设置存储在 Servlet 容器的 HttpSession 中。因此,这些设置对每个会话来说是临时的,因此当每个会话结束时都会丢失。
Note that there is no direct relationship with external session management mechanisms, such as the Spring Session
project. This SessionLocaleResolver evaluates and modifies the corresponding HttpSession attributes against the
current HttpServletRequest.
请注意,这与外部会话管理机制(如 Spring Session 项目)没有直接关系。此 SessionLocaleResolver 针对当前 HttpServletRequest
评估和修改相应的 HttpSession 属性。
(#mvc-localeresolver-interceptor)Locale Interceptor 地域拦截器
You can enable changing of locales by adding the LocaleChangeInterceptor to one of the HandlerMapping definitions.
It detects a parameter in the request and changes the locale accordingly, calling the setLocale method on the
LocaleResolver in the dispatcher’s application context. The next example shows that calls to all *.view resources
that contain a parameter named siteLanguage now changes the locale. So, for example, a request for the URL,
[https://www.sf.net/home.view?siteLanguage=nl](https://www.sf.net/home.view?siteLanguage=nl), changes the site
language to Dutch. The following example shows how to intercept the locale:
您可以通过将 LocaleChangeInterceptor 添加到 HandlerMapping 定义之一中来启用地区更改。它会检测请求中的参数并相应地更改地区,在调度器的应用程序上下文中调用
setLocale 方法。下一个示例显示,现在所有包含名为 siteLanguage 的参数的 *.view 资源调用都会更改地区。例如,对 URL
[https://www.sf.net/home.view?siteLanguage=nl](https://www.sf.net/home.view?siteLanguage=nl)
的请求现在将网站语言更改为荷兰语。以下示例显示了如何拦截地区:
(#mvc-themeresolver)1.1.11. Themes 1.1.11. 主题
You can apply Spring Web MVC framework themes to set the overall look-and-feel of your application, thereby enhancing
user experience. A theme is a collection of static resources, typically style sheets and images, that affect the visual
style of the application.
您可以将 Spring Web MVC 框架的主题应用于设置应用程序的整体外观和感觉,从而提升用户体验。主题是一组静态资源,通常是样式表和图片,它们影响应用程序的视觉风格。
(#mvc-themeresolver-defining)Defining a theme 定义一个主题
To use themes in your web application, you must set up an implementation of the
org.springframework.ui.context.ThemeSource interface. The WebApplicationContext interface extends ThemeSource but
delegates its responsibilities to a dedicated implementation. By default, the delegate is an
org.springframework.ui.context.support.ResourceBundleThemeSource implementation that loads properties files from the
root of the classpath. To use a custom ThemeSource implementation or to configure the base name prefix of the
ResourceBundleThemeSource, you can register a bean in the application context with the reserved name, themeSource.
The web application context automatically detects a bean with that name and uses it.
要使用主题在你的 Web 应用程序中,你必须设置一个实现 org.springframework.ui.context.ThemeSource 接口的实例。
WebApplicationContext 接口扩展 ThemeSource 但将责任委托给一个专门的实现。默认情况下,委托是一个从类路径根目录加载属性文件的
org.springframework.ui.context.support.ResourceBundleThemeSource 实现。要使用自定义的 ThemeSource 实现或配置
ResourceBundleThemeSource 的基本名称前缀,你可以在应用程序上下文中使用保留名称 themeSource 注册一个 bean。Web
应用程序上下文会自动检测具有该名称的 bean 并使用它。
When you use the ResourceBundleThemeSource, a theme is defined in a simple properties file. The properties file lists
the resources that make up the theme, as the following example shows:
当您使用 ResourceBundleThemeSource 时,一个主题在简单的属性文件中定义。属性文件列出了构成主题的资源,如下例所示:
styleSheet=/themes/cool/style.css background=/themes/cool/img/coolBg.jpg
The keys of the properties are the names that refer to the themed elements from view code. For a JSP, you typically do
this using the spring:theme custom tag, which is very similar to the spring:message tag. The following JSP fragment
uses the theme defined in the previous example to customize the look and feel:
属性键是引用视图代码中主题元素的名称。对于 JSP,通常使用 spring:theme 自定义标签来完成,这与 spring:message 标签非常相似。以下
JSP 片段使用前一个示例中定义的主题来自定义外观和感觉:
By default, the ResourceBundleThemeSource uses an empty base name prefix. As a result, the properties files are loaded
from the root of the classpath. Thus, you would put the cool.properties theme definition in a directory at the root of
the classpath (for example, in /WEB-INF/classes). The ResourceBundleThemeSource uses the standard Java resource
bundle loading mechanism, allowing for full internationalization of themes. For example, we could have a
/WEB-INF/classes/cool_nl.properties that references a special background image with Dutch text on it.
默认情况下, ResourceBundleThemeSource 使用一个空的基准名称前缀。因此,属性文件是从类路径的根目录加载的。因此,您应该将
cool.properties 主题定义放在类路径根目录下的一个目录中(例如,在 /WEB-INF/classes 中)。 ResourceBundleThemeSource
使用标准的 Java 资源包加载机制,允许主题完全国际化。例如,我们可以有一个 /WEB-INF/classes/cool_nl.properties
,它引用了一个带有荷兰文字的特殊背景图像。
(#mvc-themeresolver-resolving)Resolving Themes 解决主题
After you define themes, as described in the preceding section, you decide which theme to
use. The DispatcherServlet looks for a bean named themeResolver to find out which ThemeResolver implementation to
use. A theme resolver works in much the same way as a LocaleResolver. It detects the theme to use for a particular
request and can also alter the request’s theme. The following table describes the theme resolvers provided by Spring:
在您定义主题,如前文所述之后,您决定使用哪个主题。 DispatcherServlet 会查找名为 themeResolver 的 bean,以确定使用哪个
ThemeResolver 实现。主题解析器的工作方式与 LocaleResolver 类似。它检测特定请求应使用的主题,并且还可以更改请求的主题。以下表格描述了
Spring 提供的主题解析器:
Table 5. ThemeResolver implementations
表 5. ThemeResolver 实现
Class 班级
Description 描述
FixedThemeResolver
Selects a fixed theme, set by using the defaultThemeName property.
选择一个固定的主题,通过使用 defaultThemeName 属性设置。
SessionThemeResolver
The theme is maintained in the user’s HTTP session. It needs to be set only once for each session but is not persisted
between sessions.
主题保存在用户的 HTTP 会话中。每个会话只需要设置一次,但不会在会话之间持久化。
CookieThemeResolver
The selected theme is stored in a cookie on the client.
所选主题存储在客户端的 cookie 中。
Spring also provides a ThemeChangeInterceptor that lets theme changes on every request with a simple request
parameter.
Spring 还提供了一个 ThemeChangeInterceptor ,允许通过简单的请求参数在每个请求上更改主题。
(#mvc-multipart)1.1.12. Multipart Resolver
1.1.12. 多部分解析器
MultipartResolver from the org.springframework.web.multipart package is a strategy for parsing multipart requests
including file uploads. There is one implementation based
on Commons FileUpload and another based on Servlet 3.0 multipart
request parsing.
MultipartResolver 来自 org.springframework.web.multipart 包的策略用于解析包括文件上传的多部分请求。有一个基于 Commons
FileUpload 的实现,另一个基于 Servlet 3.0 多部分请求解析。
To enable multipart handling, you need to declare a MultipartResolver bean in your DispatcherServlet Spring
configuration with a name of multipartResolver. The DispatcherServlet detects it and applies it to the incoming
request. When a POST with a content type of multipart/form-data is received, the resolver parses the content wraps the
current HttpServletRequest as a MultipartHttpServletRequest to provide access to resolved files in addition to
exposing parts as request parameters.
要启用多部分处理,您需要在您的 Spring 配置中声明一个名为 multipartResolver 的 MultipartResolver bean。
DispatcherServlet 会检测它并将其应用于传入的请求。当接收到内容类型为 multipart/form-data 的 POST 请求时,解析器会解析内容,将当前的
HttpServletRequest 包装为 MultipartHttpServletRequest ,以便除了暴露部分作为请求参数外,还可以访问解析后的文件。
(#mvc-multipart-resolver-commons)Apache CommonsFileUpload
To use Apache Commons FileUpload, you can configure a bean of type CommonsMultipartResolver with a name of
multipartResolver. You also need to have the commons-fileupload jar as a dependency on your classpath.
要使用 Apache Commons FileUpload ,您可以配置一个类型为 CommonsMultipartResolver 的 bean,并为其指定名称
multipartResolver 。您还需要将 commons-fileupload jar 文件作为类路径上的依赖项。
This resolver variant delegates to a local library within the application, providing maximum portability across Servlet
containers. As an alternative, consider standard Servlet multipart resolution through the container’s own parser as
discussed below.
此解析器变体将委托给应用程序内的本地库,提供跨 Servlet 容器的最大可移植性。作为替代方案,请考虑以下所述通过容器自身解析器进行的标准
Servlet 多部分解析。
Commons FileUpload traditionally applies to POST requests only but accepts any multipart/ content type. See the
CommonsMultipartResolver
javadoc for details and configuration options.
Commons FileUpload 传统上仅适用于 POST 请求,但接受任何 multipart/ 内容类型。请参阅 CommonsMultipartResolver javadoc
以获取详细信息和管理选项。
(#mvc-multipart-resolver-standard)Servlet 3.0
Servlet 3.0 multipart parsing needs to be enabled through Servlet container configuration. To do so:
Servlet 3.0 的多部分解析需要通过 Servlet 容器配置来启用。为此:
-
In Java, set a
MultipartConfigElementon the Servlet registration.
在 Java 中,在 Servlet 注册上设置MultipartConfigElement。 -
In
web.xml, add a"<multipart-config>"section to the servlet declaration.
在web.xml中,向 servlet 声明中添加一个"<multipart-config>"部分。
The following example shows how to set a MultipartConfigElement on the Servlet registration:
以下示例展示了如何在 Servlet 注册中设置 MultipartConfigElement :
Once the Servlet 3.0 configuration is in place, you can add a bean of type StandardServletMultipartResolver with a
name of multipartResolver.
一旦 Servlet 3.0 配置就绪,您就可以添加一个类型为 StandardServletMultipartResolver 、名称为 multipartResolver 的 bean。
This resolver variant uses your Servlet container’s multipart parser as-is, potentially exposing the application to
container implementation differences. By default, it will try to parse any multipart/ content type with any HTTP
method but this may not be supported across all Servlet containers. See the
StandardServletMultipartResolver
javadoc for details and configuration options.
此解析器变体直接使用您的 Servlet 容器的 multipart 解析器,可能会使应用程序暴露于容器实现差异。默认情况下,它将尝试解析任何
HTTP 方法下的 multipart/ 内容类型,但这可能不是所有 Servlet 容器都支持。请参阅 StandardServletMultipartResolver
javadoc 以获取详细信息和管理选项。
(#mvc-logging)1.1.13. Logging 1.1.13. 日志记录
DEBUG-level logging in Spring MVC is designed to be compact, minimal, and human-friendly. It focuses on high-value bits
of information that are useful over and over again versus others that are useful only when debugging a specific issue.
Spring MVC 中的 DEBUG 级别日志设计得紧凑、简洁且易于阅读。它侧重于那些反复有用的有价值信息,而不是那些仅在调试特定问题时才有用的信息。
TRACE-level logging generally follows the same principles as DEBUG (and, for example, also should not be a fire hose)
but can be used for debugging any issue. In addition, some log messages may show a different level of detail at TRACE
versus DEBUG.
跟踪级别的日志通常遵循与 DEBUG 相同的准则(例如,也不应该是信息洪流),但可以用于调试任何问题。此外,一些日志消息在 TRACE 与
DEBUG 之间可能显示不同级别的详细信息。
Good logging comes from the experience of using the logs. If you spot anything that does not meet the stated goals,
please let us know.
良好的日志记录来自使用日志的经验。如果您发现任何不符合所述目标的内容,请告知我们。
(#mvc-logging-sensitive-data)Sensitive Data 敏感数据
DEBUG and TRACE logging may log sensitive information. This is why request parameters and headers are masked by default
and their logging in full must be enabled explicitly through the enableLoggingRequestDetails property on
DispatcherServlet.
调试和跟踪日志可能会记录敏感信息。这就是为什么请求参数和默认情况下会被屏蔽,并且它们的完整日志记录必须通过在
DispatcherServlet 上的 enableLoggingRequestDetails 属性显式启用。
The following example shows how to do so by using Java configuration:
以下示例展示了如何通过使用 Java 配置来实现: