6. 使用 Object-XML Mapper 进行 XML 编排
预计阅读时间: 21 分钟(#oxm-introduction)6.1. Introduction 6.1. 简介
This chapter, describes Spring’s Object-XML Mapping support. Object-XML Mapping (O-X mapping for short) is the act of
converting an XML document to and from an object. This conversion process is also known as XML Marshalling, or XML
Serialization.
本章描述了 Spring 的对象-XML 映射支持。对象-XML 映射(简称 O-X 映射)是将 XML 文档转换为对象以及从对象转换回 XML
文档的过程。此转换过程也被称为 XML 打包或 XML 序列化。
This chapter uses these terms interchangeably.
本章使用这些术语互为替换。
Within the field of O-X mapping, a marshaller is responsible for serializing an object (graph) to XML. In similar
fashion, an unmarshaller deserializes the XML to an object graph. This XML can take the form of a DOM document, an input
or output stream, or a SAX handler.
在 O-X 映射领域,一个 marshaller 负责将对象(图)序列化为 XML。类似地,一个 unmarshaller 将 XML 反序列化为对象图。这种 XML
可以采取 DOM 文档、输入或输出流或 SAX 处理器的形式。
Some of the benefits of using Spring for your O/X mapping needs are:
使用 Spring 满足您的 O/X 映射需求的一些好处包括:
(#oxm-ease-of-configuration)6.1.1. Ease of configuration
6.1.1. 配置简便
Spring’s bean factory makes it easy to configure marshallers, without needing to construct JAXB context, JiBX binding
factories, and so on. You can configure the marshallers as you would any other bean in your application context.
Spring 的 Bean 工厂使得配置 marshaller 变得简单,无需构建 JAXB 上下文、JiBX 绑定工厂等。您可以在应用程序上下文中像配置任何其他
bean 一样配置 marshaller。
Additionally, XML namespace-based configuration is available for a number of marshallers, making the configuration even
simpler.
此外,许多 marshaller 支持基于 XML 命名空间的配置,使配置更加简单。
(#oxm-consistent-interfaces)6.1.2. Consistent Interfaces
6.1.2. 一致接口
Spring’s O-X mapping operates through two global interfaces:
Marshaller
and
Unmarshaller.
These abstractions let you switch O-X mapping frameworks with relative ease, with little or no change required on the
classes that do the marshalling.
春季的 O-X 映射通过两个全局接口操作: Marshaller 和 Unmarshaller 。这些抽象允许您相对容易地切换 O-X
映射框架,对进行序列化的类几乎没有或不需要更改。
This approach has the additional benefit of making it possible to do XML marshalling with a mix-and-match approach (for
example, some marshalling performed using JAXB and some by XStream) in a non-intrusive fashion, letting you use the
strength of each technology.
这种方法还具有额外的好处,即能够以混合匹配的方式(例如,一些序列化操作使用 JAXB 完成,一些使用 XStream 完成)以非侵入性方式进行
XML 序列化,让您能够利用每种技术的优势。
(#oxm-consistent-exception-hierarchy)6.1.3. Consistent Exception Hierarchy
6.1.3. 一致的异常层次结构
Spring provides a conversion from exceptions from the underlying O-X mapping tool to its own exception hierarchy with
the XmlMappingException as the root exception. These runtime exceptions wrap the original exception so that no
information is lost.
Spring 将底层 O-X 映射工具的异常转换为自身的异常层次结构,以 XmlMappingException 作为根异常。这些运行时异常封装了原始异常,以确保不丢失任何信息。
(#oxm-marshaller-unmarshaller)6.2.Marshaller andUnmarshaller 6.2.Marshaller 和Unmarshaller
As stated in the introduction, a marshaller serializes an object to XML, and an unmarshaller
deserializes XML stream to an object. This section describes the two Spring interfaces used for this purpose.
如引言所述,marshaller 将对象序列化为 XML,而 unmarshaller 将 XML 流反序列化为对象。本节描述了用于此目的的两个 Spring 接口。
(#oxm-marshaller)6.2.1. UnderstandingMarshaller 6.2.1. 理解Marshaller
Spring abstracts all marshalling operations behind the org.springframework.oxm.Marshaller interface, the main method
of which follows:
Spring 将所有序列化操作抽象在 org.springframework.oxm.Marshaller 接口之后,其主方法遵循以下模式:
The Marshaller interface has one main method, which marshals the given object to a given javax.xml.transform.Result.
The result is a tagging interface that basically represents an XML output abstraction. Concrete implementations wrap
various XML representations, as the following table indicates:
Marshaller 接口有一个主要方法,该方法将给定的对象封装到给定的 javax.xml.transform.Result 中。结果是代表 XML
输出抽象的标记接口。具体实现封装了各种 XML 表示,如下表所示:
Result implementation 结果实施
Wraps XML representation
包装 XML 表示
DOMResult
org.w3c.dom.Node
SAXResult
org.xml.sax.ContentHandler
StreamResult
java.io.File, java.io.OutputStream, or java.io.Writer
java.io.File , java.io.OutputStream 或 java.io.Writer
Although the marshal() method accepts a plain object as its first parameter, most Marshaller implementations cannot
handle arbitrary objects. Instead, an object class must be mapped in a mapping file, be marked with an annotation, be
registered with the marshaller, or have a common base class.
尽管 marshal() 方法接受一个普通对象作为其第一个参数,但大多数 Marshaller 实现无法处理任意对象。相反,必须在映射文件中映射对象类,用注解标记,注册给
marshaller,或者有一个公共基类。
Refer to the later sections in this chapter to determine how your O-X technology manages this.
参考本章后续部分以确定您的 O-X 技术如何处理此问题。
(#oxm-unmarshaller)6.2.2. UnderstandingUnmarshaller 6.2.2. 理解Unmarshaller
Similar to the Marshaller, we have the org.springframework.oxm.Unmarshaller interface, which the following listing
shows:
类似于 Marshaller ,我们还有 org.springframework.oxm.Unmarshaller 接口,以下列表展示了该接口:
This interface also has one method, which reads from the given javax.xml.transform.Source (an XML input abstraction)
and returns the object read. As with Result, Source is a tagging interface that has three concrete implementations.
Each wraps a different XML representation, as the following table indicates:
此接口还有一个方法,该方法从给定的 javax.xml.transform.Source (一个 XML 输入抽象)中读取并返回读取的对象。与 Result 一样,
Source 是一个标记接口,有三个具体实现。每个实现都封装了不同的 XML 表示,如下表所示:
Source implementation 源实现
Wraps XML representation
包装 XML 表示
DOMSource
org.w3c.dom.Node
SAXSource
org.xml.sax.InputSource, and org.xml.sax.XMLReader``org.xml.sax.InputSource ,和 org.xml.sax.XMLReader
StreamSource
java.io.File, java.io.InputStream, or java.io.Reader
java.io.File , java.io.InputStream 或 java.io.Reader
Even though there are two separate marshalling interfaces (Marshaller and Unmarshaller), all implementations in
Spring-WS implement both in one class. This means that you can wire up one marshaller class and refer to it both as a
marshaller and as an unmarshaller in your applicationContext.xml.
尽管存在两个独立的序列化接口( Marshaller 和 Unmarshaller ),Spring-WS 中的所有实现都在一个类中实现了这两个接口。这意味着您可以在您的
applicationContext.xml 中连接一个序列化类,并将其同时作为序列化器和反序列化器使用。
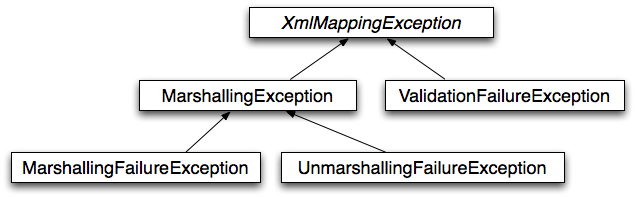
(#oxm-xmlmappingexception)6.2.3. UnderstandingXmlMappingException 6.2.3. 理解XmlMappingException
Spring converts exceptions from the underlying O-X mapping tool to its own exception hierarchy with the
XmlMappingException as the root exception. These runtime exceptions wrap the original exception so that no information
will be lost.
Spring 将底层 O-X 映射工具的异常转换为自身的异常层次结构,以 XmlMappingException 作为根异常。这些运行时异常封装了原始异常,以确保不会丢失任何信息。
Additionally, the MarshallingFailureException and UnmarshallingFailureException provide a distinction between
marshalling and unmarshalling operations, even though the underlying O-X mapping tool does not do so.
此外, MarshallingFailureException 和 UnmarshallingFailureException 在序列化和反序列化操作之间提供了区分,尽管底层的
O-X 映射工具并没有这样做。
The O-X Mapping exception hierarchy is shown in the following figure:
O-X 映射异常层次结构如图所示:
(#oxm-usage)6.3. UsingMarshaller andUnmarshaller
6.3. 使用 Marshaller 和 Unmarshaller
You can use Spring’s OXM for a wide variety of situations. In the following example, we use it to marshal the settings
of a Spring-managed application as an XML file. In the following example, we use a simple JavaBean to represent the
settings:
您可以使用 Spring 的 OXM 处理各种情况。在以下示例中,我们将其用于将 Spring 管理的应用程序的设置序列化为 XML
文件。在以下示例中,我们使用一个简单的 JavaBean 来表示设置:
The application class uses this bean to store its settings. Besides a main method, the class has two methods:
saveSettings() saves the settings bean to a file named settings.xml, and loadSettings() loads these settings
again. The following main() method constructs a Spring application context and calls these two methods:
应用程序类使用此 Bean 来存储其设置。除了主方法外,该类还有两个方法: saveSettings() 将设置 Bean 保存到名为 settings.xml
的文件中,以及 loadSettings() 再次加载这些设置。以下 main() 方法构建 Spring 应用程序上下文并调用这两个方法:
The Application requires both a marshaller and an unmarshaller property to be set. We can do so by using the
following applicationContext.xml:
该 Application 需要设置一个 marshaller 和一个 unmarshaller 属性。我们可以通过以下 applicationContext.xml 来实现:
This application context uses XStream, but we could have used any of the other marshaller instances described later in
this chapter. Note that, by default, XStream does not require any further configuration, so the bean definition is
rather simple. Also note that the XStreamMarshaller implements both Marshaller and Unmarshaller, so we can refer
to the xstreamMarshaller bean in both the marshaller and unmarshaller property of the application.
此应用程序上下文使用 XStream,但我们本可以使用本章后面描述的任何其他 marshaller 实例。请注意,默认情况下,XStream
不需要任何进一步配置,因此 bean 定义相当简单。另外请注意, XStreamMarshaller 实现了 Marshaller 和 Unmarshaller
,因此我们可以同时在应用程序的 marshaller 和 unmarshaller 属性中引用 xstreamMarshaller bean。
This sample application produces the following settings.xml file:
此示例应用程序生成以下 settings.xml 文件:
(#oxm-schema-based-config)6.4. XML Configuration Namespace
6.4. XML 配置命名空间
You can configure marshallers more concisely by using tags from the OXM namespace. To make these tags available, you
must first reference the appropriate schema in the preamble of the XML configuration file. The following example shows
how to do so:
您可以通过使用 OXM 命名空间中的标签来更简洁地配置序列化器。为了使这些标签可用,您必须首先在 XML
配置文件的序言中引用适当的模式。以下示例显示了如何这样做:
1
Reference the oxm schema.
引用 oxm 架构。
2
Specify the oxm schema location.
指定 oxm 架构位置。
The schema makes the following elements available:
该模式提供了以下元素:
Each tag is explained in its respective marshaller’s section. As an example, though, the configuration of a JAXB2
marshaller might resemble the following:
每个标签都在其各自的 marshaller 部分进行解释。例如,JAXB2 marshaller 的配置可能类似于以下内容:
(#oxm-jaxb)6.5. JAXB
The JAXB binding compiler translates a W3C XML Schema into one or more Java classes, a jaxb.properties file, and
possibly some resource files. JAXB also offers a way to generate a schema from annotated Java classes.
JAXB 绑定编译器将 W3C XML 模式转换为一个或多个 Java 类、一个 jaxb.properties 文件以及可能的一些资源文件。JAXB 还提供了一种从注解
Java 类生成模式的方法。
Spring supports the JAXB 2.0 API as XML marshalling strategies, following the Marshaller and Unmarshaller interfaces
described in Marshaller and Unmarshaller. The corresponding integration classes
reside in the org.springframework.oxm.jaxb package.
Spring 支持 JAXB 2.0 API 作为 XML 序列化策略,遵循 Marshaller 和 Unmarshaller 中描述的 Marshaller 和 Unmarshaller
接口。相应的集成类位于 org.springframework.oxm.jaxb 包中。
(#oxm-jaxb2)6.5.1. UsingJaxb2Marshaller 6.5.1. 使用Jaxb2Marshaller
The Jaxb2Marshaller class implements both of Spring’s Marshaller and Unmarshaller interfaces. It requires a
context path to operate. You can set the context path by setting the contextPath property. The context path is a list
of colon-separated Java package names that contain schema derived classes. It also offers a classesToBeBound property,
which allows you to set an array of classes to be supported by the marshaller. Schema validation is performed by
specifying one or more schema resources to the bean, as the following example shows:
该 Jaxb2Marshaller 类实现了 Spring 的 Marshaller 和 Unmarshaller 接口。它需要一个上下文路径才能运行。您可以通过设置
contextPath 属性来设置上下文路径。上下文路径是一系列以冒号分隔的 Java 包名,其中包含从模式派生出的类。它还提供了一个
classesToBeBound 属性,允许您设置一个由 marshaller 支持的类数组。通过将一个或多个模式资源指定给 bean,执行模式验证,如下例所示:
(#oxm-jaxb2-xsd)XML Configuration Namespace
XML 配置命名空间
The jaxb2-marshaller element configures a org.springframework.oxm.jaxb.Jaxb2Marshaller, as the following example
shows:
jaxb2-marshaller 元素配置了一个 org.springframework.oxm.jaxb.Jaxb2Marshaller ,如下例所示:
Alternatively, you can provide the list of classes to bind to the marshaller by using the class-to-be-bound child
element:
或者,您可以通过使用 class-to-be-bound 子元素来提供要绑定到 marshaller 的类列表:
The following table describes the available attributes:
以下表格描述了可用的属性:
Attribute 属性
Description 描述
Required 必需的
id
The ID of the marshaller
The ID of the marshaller 该打包器的 ID
No 没有
contextPath
The JAXB Context path JAXB 上下文路径
No 没有
(#oxm-jibx)6.6. JiBX
The JiBX framework offers a solution similar to that which Hibernate provides for ORM: A binding definition defines the
rules for how your Java objects are converted to or from XML.
JiBX 框架提供了一个类似于 Hibernate 为 ORM 提供的解决方案:绑定定义定义了如何将 Java 对象转换为或从 XML 转换的规则。
After preparing the binding and compiling the classes, a JiBX binding compiler enhances the class files and adds code to
handle converting instances of the classes from or to XML.
在准备绑定和编译类之后,一个 JiBX 绑定编译器增强了类文件,并添加了处理将类的实例从或转换为 XML 的代码。
For more information on JiBX, see the JiBX web site. The Spring integration classes
reside in the org.springframework.oxm.jibx package.
关于 JiBX 的更多信息,请参阅 JiBX 网站。Spring 集成类位于 org.springframework.oxm.jibx 包中。
(#oxm-jibx-marshaller)6.6.1. UsingJibxMarshaller 6.6.1. 使用JibxMarshaller
The JibxMarshaller class implements both the Marshaller and Unmarshaller interface. To operate, it requires the
name of the class to marshal in, which you can set using the targetClass property. Optionally, you can set the binding
name by setting the bindingName property. In the following example, we bind the Flights class:
该 JibxMarshaller 类实现了 Marshaller 和 Unmarshaller 接口。要操作,它需要传入类的名称,您可以使用 targetClass
属性来设置。可选地,您可以通过设置 bindingName 属性来设置绑定名称。在以下示例中,我们绑定了 Flights 类:
A JibxMarshaller is configured for a single class. If you want to marshal multiple classes, you have to configure
multiple JibxMarshaller instances with different targetClass property values.
一个 JibxMarshaller 配置用于单个类。如果您想序列化多个类,您必须配置具有不同 targetClass 属性值的多个 JibxMarshaller
实例。
(#oxm-jibx-xsd)XML Configuration Namespace
XML 配置命名空间
The jibx-marshaller tag configures a org.springframework.oxm.jibx.JibxMarshaller, as the following example shows:
jibx-marshaller 标签配置了一个 org.springframework.oxm.jibx.JibxMarshaller ,如下例所示:
The following table describes the available attributes:
以下表格描述了可用的属性:
Attribute 属性
Description 描述
Required 必需的
id
The ID of the marshaller
The ID of the marshaller 该打包器的 ID
No 没有
target-class
The target class for this marshaller
目标类为此编解码器
Yes 是的
bindingName
The binding name used by this marshaller
该 marshaller 使用的绑定名称
No 没有
(#oxm-xstream)6.7. XStream
XStream is a simple library to serialize objects to XML and back again. It does not require any mapping and generates
clean XML.
XStream 是一个简单的库,可以将对象序列化为 XML,然后再将其反序列化。它不需要任何映射,并生成干净的 XML。
For more information on XStream, see the XStream web site. The Spring integration classes
reside in the org.springframework.oxm.xstream package.
关于 XStream 的更多信息,请参阅 XStream 网站。Spring 集成类位于 org.springframework.oxm.xstream 包中。
(#oxm-xstream-marshaller)6.7.1. UsingXStreamMarshaller 6.7.1. 使用XStreamMarshaller
The XStreamMarshaller does not require any configuration and can be configured in an application context directly. To
further customize the XML, you can set an alias map, which consists of string aliases mapped to classes, as the
following example shows:
follows the XStreamMarshaller does not require any configuration and can be configured in an application context
directly. To further customize the XML, you can set an alias map, which consists of string aliases mapped to classes, as
the following example shows:
By default, XStream lets arbitrary classes be unmarshalled, which can lead to unsafe Java serialization effects. As
such, we do not recommend using the XStreamMarshaller to unmarshal XML from external sources (that is, the Web), as
this can result in security vulnerabilities.
默认情况下,XStream 允许任意类进行反序列化,这可能导致不安全的 Java 序列化效果。因此,我们不推荐使用 XStreamMarshaller
从外部来源(即网络)反序列化 XML,因为这可能导致安全漏洞。
If you choose to use the XStreamMarshaller to unmarshal XML from an external source, set the supportedClasses
property on the XStreamMarshaller, as the following example shows:
如果您选择使用 XStreamMarshaller 从外部源反序列化 XML,请设置 XStreamMarshaller 上的 supportedClasses 属性,如下例所示:
Doing so ensures that only the registered classes are eligible for unmarshalling.
这样做确保只有注册的类才有资格进行反序列化。
Additionally, you can
register custom converters
to make sure that only your supported classes can be unmarshalled. You might want to add a CatchAllConverter as the
last converter in the list, in addition to converters that explicitly support the domain classes that should be
supported. As a result, default XStream converters with lower priorities and possible security vulnerabilities do not
get invoked.
此外,您还可以注册自定义转换器以确保只有您支持的类可以被反序列化。您可能希望在列表的末尾添加一个 CatchAllConverter
作为最后一个转换器,除了显式支持应支持的域类之外。因此,默认的 XStream 转换器(优先级较低且可能存在安全漏洞)不会触发。
Note that XStream is an XML serialization library, not a data binding library. Therefore, it has limited namespace
support. As a result, it is rather unsuitable for usage within Web Services.
请注意,XStream 是一个 XML 序列化库,而不是数据绑定库。因此,它对命名空间的兼容性有限。因此,它不太适合在 Web 服务中使用。